Mobile automation testing quality heavily relies on the correct identification of screen elements. The tool Appium allows easier element identification through multiple identification strategies. Whether you’re testing on real devices or using an Android emulator Mac, accurate element matching remains critical. Regular Expressions (Regex) represent a sophisticated tool that provides the most powerful capability to enhance element matching. Objectives of this blog post include studying Regular Expressions fundamentals within Appium while demonstrating practical element-matching strategies.
What are Regular Expressions?
The search pattern called Regular Expressions goes by its common name, Regex, and exists as a sequential character sequence. A single pattern serves as a tool to find text content match patterns, or replace them in strings. Regular Expressions bring brilliance through their ability to execute complex queries that basic string-matching methods would find impossible.
The search pattern format enables you to locate various phone numbers and email addresses in your documents. The regex pattern allows users to detect particular sequences, such as “xxxx-xxx-xxxx” for phone numbers, alongside “username@domain.com” for email addresses.
Why Use Regular Expressions in Appium?
When performing tests on mobile applications, the automated manipulation of user interface elements stands as a crucial requirement. The standard procedure for UI element detection in Appium requires test scripts to indicate the id, class, or name properties. Working with this approach becomes inefficient for developers when dealing with dynamic content in combination with complex user interfaces. The measurement tool Regular Expressions functions within Appium because the tool enables flexible element matching through Regex, making it a vital part of android automation.
Organizations can use pattern-based element identification through Regular Expressions to make their tests more adaptive to changes in the user interface and adapt themselves to different application variations. Regex can find the text of elements with foreseeable patterns if the UI structure changes unexpectedly.
Using Regex in Appium enables:
- Faster UI updates: Instead of adjusting multiple tests after every UI change, you can use Regex to locate elements based on flexible patterns.
- Handling Dynamic Content: Regex helps in handling dynamic data (like timestamps, version numbers, and random strings) that might change every time the application runs.
- Improved Test Resilience: When element identifiers change frequently, Regex-based patterns can allow for greater tolerance and accuracy in element matching.
How Regular Expressions Help in Element Matching
Element matching in Appium often requires specifying identifiers or attributes of the UI elements. Testers sometimes depend on exact strings for text or class names and accessibility IDs when performing traditional testing. These application identifiers may experience changes in stability or consistency when compared between different versions of the app and different device platforms.
Example Scenarios:
- Dynamic Text Labels: The mobile application displays text labels that adapt based on language preference together with a current time frame and individual user profiles.
- Dynamic Element IDs: The id of a UI element often contains randomly generated strings together with timestamps, which result in unpredictable matching outcomes for static identification.
Regular Expressions create a solution that enables pattern recognition to perform matches. Appium can function with pattern-based matching instead of exact value searching because it looks for elements that suit various potential value combinations.
For instance:
- When dealing with element IDs that use btn_12345, btn_67890, and btn_abcde patterns, you can rely on the regular expression ^btn_\d+ to identify IDs that start with btn_ followed by multiple digits.
- Element matching can be performed through patterns using ^Welcome, User .*, which matches all text that starts with “Welcome, User” followed by any character sequence.
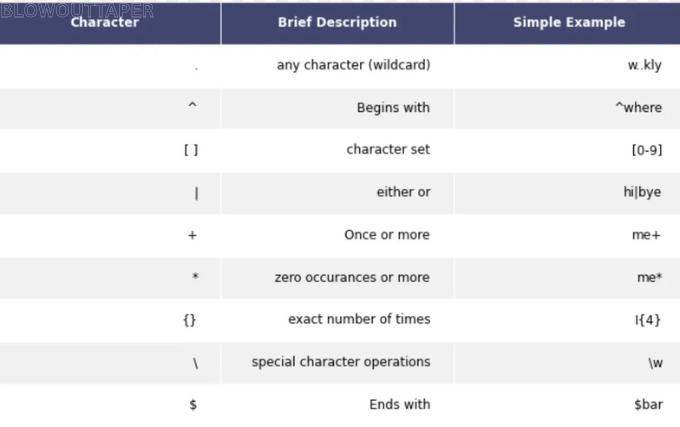
Common Regular Expression Syntax and Patterns
Comprehension of basic Regular Expression syntax for Appium requires understanding before moving forward with practical examples.
- Dot (.): Matches any single character except for newlines.
- Example: a.c matches abc, axc, a c, etc.
- Asterisk (*): Matches 0 or more occurrences of the preceding character or group.
- Example: a*b matches b, ab, aab, aaab, etc.
- Caret (^): Matches the beginning of a string.
- Example: ^abc matches abc but not xabc.
- Dollar Sign ($): Matches the end of a string.
- Example: abc$ matches abc but not xabc.
- Square Brackets [ ]: Matches any one character within the brackets.
- Example: [abc] matches a, b, or c.
- Parentheses (): Used for grouping expressions.
- Example: (ab)+ matches ab, abab, etc.
- Question Mark (?): Matches 0 or 1 occurrence of the preceding character.
- Example: a?b matches b or ab.
- Pipe (|): Represents a logical OR.
- Example: abc|def matches either abc or def.
Using Regular Expressions in Appium for Element Matching
After reviewing Regular Expressions basics we will see their application in Appium element matching operations.
Example 1: Matching Based on Partial Text
In many scenarios, elements contain dynamic text that changes depending on the context. Through Regex you can find elements by entering only part of their text instead of requiring the complete full strings.
During the testing of a mobile application containing a button with time-dependent text content, you would evaluate. When the device operates day or night, the button text reads either “Good Morning” or “Good Evening.” A Regular Expression pattern can substitute traditional explicit matching procedures since it functions to match the initial section of a string.
button = driver.find_element_by_ios_predicate(“type == ‘XCUIElementTypeButton’ AND name MATCHES ‘Good.*'”)
The MATCHES operator in the iOS predicate enables Regular Expression matching that covers the entire text sequence starting with “Good”, thus providing compatibility for both “Good Morning” and “Good Evening”.
Example 2: Matching Attributes Dynamically
Appium allows you to search for elements based on various attributes like id, class, or name. The temporary challenge of dynamic attribute changes (such as multiple items in lists) can be solved by using Regex.
A list of buttons exists with IDs starting from button_12345 up to button_67890 and all other possible following numbers. A Regular Expression follows the pattern “button_” then permits an unlimited number of digits in the ID.
button = driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator(‘new UiSelector().resourceIdMatches(“com.example:id/button_\\d+”)’)
The pattern identifies any resource IDs beginning with button_ then employing any number of digits.
Best Practices for Using Regex in Appium
To implement Appium test automation successfully through Regular Expressions, adopt the following practices for optimized effectiveness and efficiency:
- Use Anchors Wisely: The search prioritization improves by using anchoring operators ^ (beginning of string) and $ (end of string) to define search section boundaries, which enhances test reliability.
- Avoid Overuse: Application tests become harder to read and maintain when Regular Expressions have excessive use in tests. Only use Regular Expressions when dealing with dynamic content because they provide the most benefit.
- Keep It Simple: Try to write simple patterns that are easy to understand. Complex expressions can lead to bugs and are difficult to debug.
- Test Your Regex Patterns: Always test your Regular Expressions before using them in your test scripts. There are many online Regex testers available to verify your patterns.
- Optimize for Performance: Regex operations can be costly in terms of performance, especially with large datasets. Ensure your expressions are optimized to avoid unnecessary backtracking, which can slow down the test execution. Use non-capturing groups (?:…) and lazy quantifiers *? or +? when appropriate to improve performance.
- Avoid Using Wildcards Too Generously: There are two problems when using the Regex wildcard dot (.) excessively, as it matches any character, resulting in unintentional outcomes. Your tests will become more accurate through precise pattern definitions, which include fixed characters or range values.
- Use Regex Flags for Case Sensitivity or Global Matching: Take advantage of the Regex i flag for case-insensitive matches or g flag for performing global search operations. Regular expressions become more flexible and reliable when you apply Regex flags, which enable them to handle multiple occurrences and various circumstances during operation.
- Be Mindful of Maintenance and Readability: The complexity of Regular Expressions grows throughout time which creates challenges for team members who need to update or comprehend them. You should also include comments with clarity and choose meaningful variable names to improve the maintenance capabilities of your Regex patterns. Refactor patterns that become too complicated.
- Use Regex for Validation, Not for Parsing: The purpose of Regex should be limited to validating input and performing pattern-matching functions, but it is inadequate for data extraction. Apply specific parsing methods that come with the Appium framework or select the proper parser to handle these tasks.
- Handle Edge Cases and Escape Properly: Testing Regular Expressions against empty strings and unexpected characters, as well as boundary cases should always be done properly while handling edge cases. The implementation of escaping techniques for special characters should receive careful examination specifically regarding \, . | characters.
Limitations and Pitfalls
The capabilities of Regular Expressions dominate many situations, but users should understand their limited capabilities and potential problems. Following several guidelines will help you work effectively with Regular Expressions:
- Performance Issues: Regex evaluation proves expensive for computers when processing significant quantities of information. If the app contains a large number of elements, overly complex regular expressions might slow down the execution of your tests.
- Overfitting: Sometimes, Regex can match more than intended, which could lead to false positives. Always ensure your patterns are well-defined.
- Platform-Specific Variations: The runtime behavior of Regular Expressions inside Appium differs between Android and iOS devices because of platform-specific constraints together with syntactic variations.
The main challenge when deploying Regex in Appium testing involves guaranteeing test success among varying devices combined with screen sizes alongside operating system versions. Since UI elements can behave differently across platforms, it’s important to test your Regex-based element matching thoroughly. LambdaTest can help overcome this limitation by allowing you to run tests on a wide range of real devices, ensuring that your Regex patterns work as expected in various configurations.
Additionally, LambdaTest provides parallel test execution, enabling you to run multiple Appium tests simultaneously across different devices. It ensures faster validation of your Regex patterns and can help in scaling your automation efforts. With LambdaTest, you can access real devices in the cloud, making it easier to test on various Android and iOS devices without maintaining a real device lab.
By running your tests on LambdaTest’s cloud grid, you eliminate the need for device management and configuration while gaining confidence that your Regex-based element matching works seamlessly across diverse real-world scenarios.
In Conclusion
Using Regular Expressions in Appium tests will boost your element matching capabilities for more flexible testing of dynamic content alongside frequent UI element modifications. Testers who use Regex can create robust test scripts that maintain stability when the application user interface changes because they require minimal script updates. The use of Regex should be strategic because excessive or complicated patterns lead to difficult test maintenance and debugging.
The appropriate usage of Regex enables faster validation testing across multiple devices and configurations through its combination with LambdaTest cloud-based device testing thus improving automation efficiency and testing reliability. Appium professionals who excel at Regular Expressions will create mobile test automation that offers long-term stability alongside scalability for present and upcoming app development hurdles.
Modern dynamic mobile interfaces demand smart, flexible testing automation, which produces higher importance as applications progress in their evolution. Tests benefit from Regular Expressions as a necessary tool that helps them adjust to changes while removing the need for costly manual updates. The implementation of Regex within your Appium test strategy enables test durability and strength while improving the testing process’s effectiveness. Testers maintain a higher focus on test content while writing tests when this methodology is utilized, thus producing a process that delivers better reliability and enhanced workflow efficiency.